GBIF Issues & Flags
Publishers share datasets, but also manage data quality. GBIF provides access to the use of biodiversity data, but also flags suspicious or missing content. Users use data, but also clean and remove records. Each play an important role in managing and improving data quality..
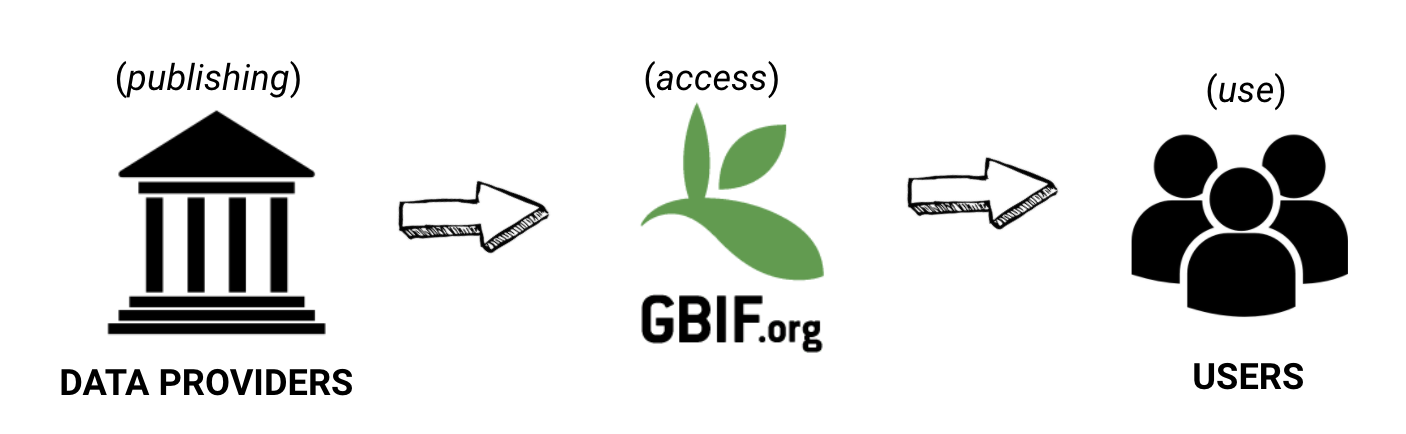
What are GBIF issues and flags?
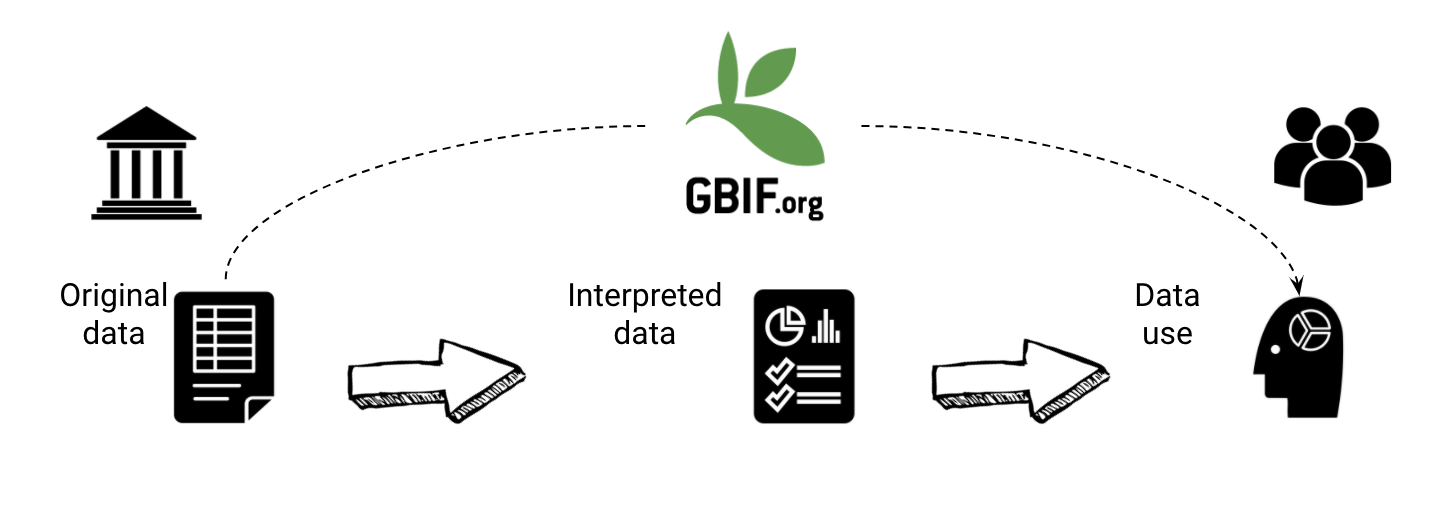
The GBIF network publishes datasets, integrating them into a common access system. Here users can retrieve data through common search and download services. During the indexation process over the raw data, GBIF adds issues and flags to records with common data quality problems.
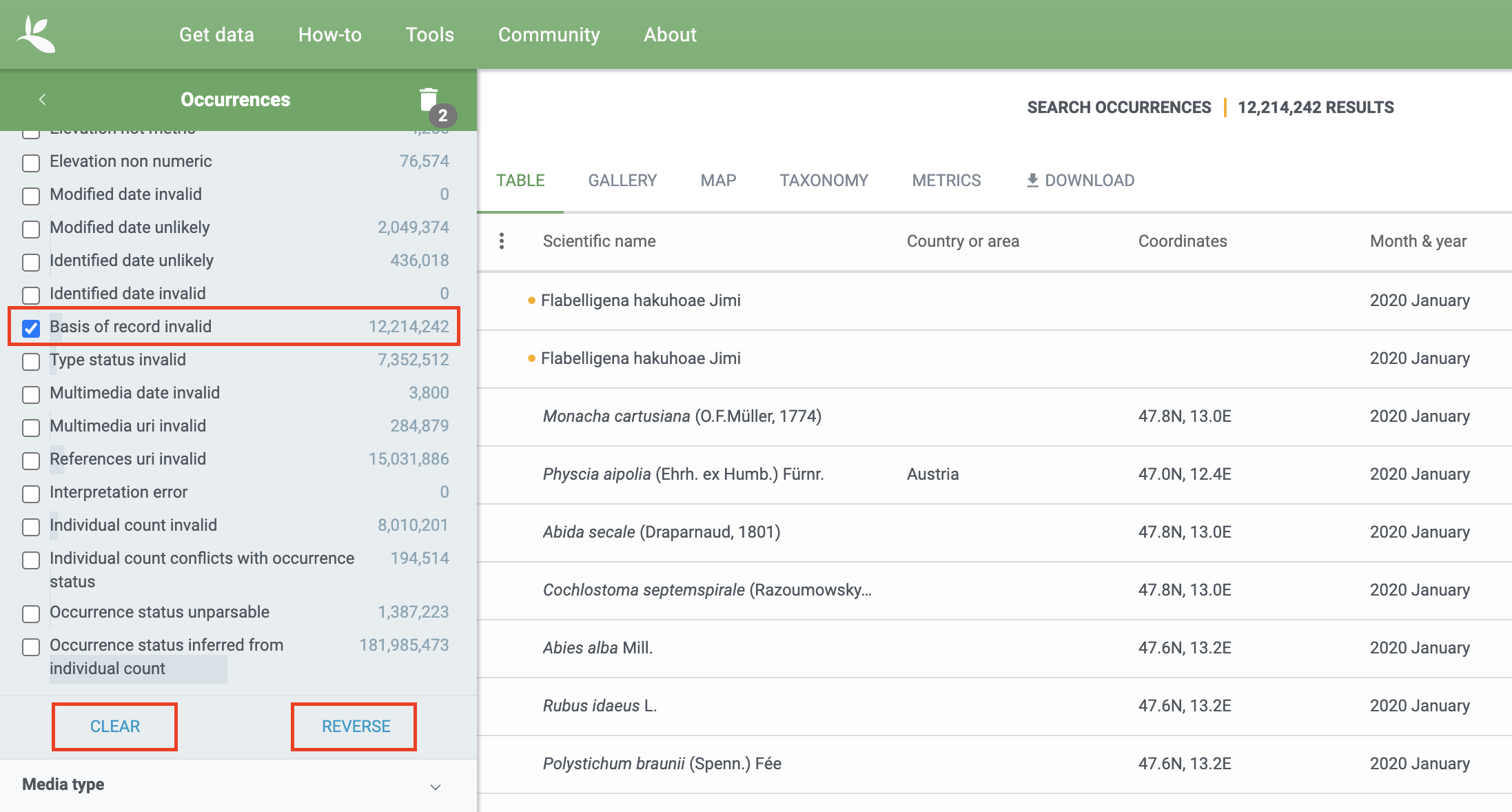
Excluding all records with a particular issue is not currently possible with the search interface. It is possible to filter all records you are not interested in with issues by selecting the particular issue and hitting the reverse button. However, reversing will still only give you all other flagged occurrences and not issue-free records. This is something that GBIF is working to improve. (at occurrence search)
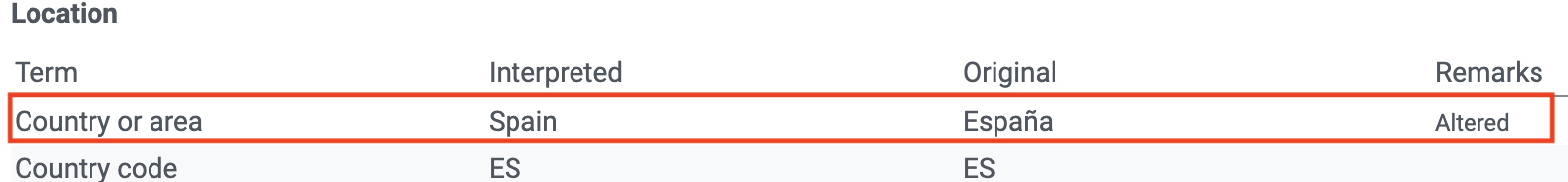
Remarks are shown on the individual occurrence pages to explain the process done after interpretation:
- Excluded means the original data couldn’t be interpreted, so is excluded in the interpreted fields.
- Altered means the original data is modified in the interpretation process to be indexed in GBIF.org.
- Inferred means the Using other record information the data indexed is inferred, if the original is empty.


The following table highlights some common geospatial issues and instructs how to fix them.
| Issue & flag | Action to take |
|---|---|
| Country derived from coordinates | Fill in the columns countryCode and country with the country information where the record was registered, following the officially ISO 3166-1-alpha-2 country code |
| Recorded date invalid | Use existing valid dates in the columns eventDate, year, month, day, following the format ISO 8601-1:2019 (YYYY-MM-DD) |
| Basis of record invalid | Use a valid Basis of Record in the column basisOfRecord, according to the nature of the record. Follow the controlled vocabulary present on this list https://rs.gbif.org/vocabulary/dwc/basis_of_record.xml |
| Country coordinate mismatch | Make sure coordinates (decimalLatitudedecimalLongitude), fall inside the indicated country (i.e. country countryCode). The country and countryCode must match and be documented following the officially ISO 3166-1-alpha-2. |
| Zero coordinate | Leave decimalLatitude and decimalLongitude blank if the coordinates are missing. Don't use "0" as a coordinate value in both columns unless your record be present there (Null Island https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Null_Island). |
| Coordinate invalid | Make sure coordinates are valid numeric decimal values. decimalLatitude: legal values lie between -90 and 90, inclusive. and decimalLongitude: legal values lie between -180 and 180, inclusive. Also, verbatimCoordinates have to be valid values for coordinates in decimal degrees, degrees decimal minutes, degrees minutes second |
## Definitions
More than 50 issues and flags have been created to deal with common data quality problems. The following long section compiles all of them and offers a more clear description of each one. This section is intended to serve as a placeholder until more formal documentation can be written.
Geospatial Issues
Zero coordinate (geospatial) example
Coordinates are exactly 0/0, often indicating an actual null coordinate.
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Country coordinate mismatch (geospatial) example
The interpreted occurrence coordinates fall outside of the indicated country.
Terms: dwc:countryCode, dwc:country, dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Coordinate invalid (geospatial) example
A coordinate value is given in some form, but GBIF is unable to interpret it. Possible reasons include, i.a., coordinates that fall out of range (larger/lower than 90/-90 or 180/-180, depending) or text values that cannot be interpreted.
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude, dwc:verbatimCoordinates, dwc:verbatimLatitude, dwc:verbatimLongitude
Coordinate out of range (geospatial) example
The supplied coordinates lie outside of the range for decimal lat/lon values (-90/90, -180/180).
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude, dwc:verbatimCoordinates, dwc:verbatimLatitude, dwc:verbatimLongitude
These 4 issues are removed by default when including coordinates and not clicking the check box:
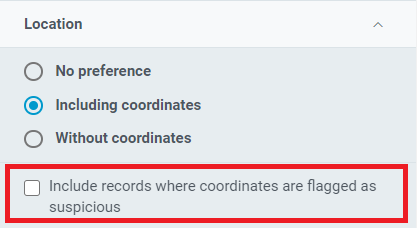
Geodetic datum assumed WGS84 (geospatial) example
If the datum is null, data interpretation assumes the record coordinates are in WGS84.
Terms: dwc:geodeticDatum
Geodetic datum invalid (geospatial) example
The geodetic datum could not be interpreted, because the supplied term cannot be matched against the vocabulary of known values.
Terms: dwc:geodeticDatum
Country mismatch (geospatial) example
Interpreted Country and Country code contradict each other.
Terms: dwc:countryCode, dwc:country
Country derived from coordinates (geospatial) example
If the country and country code are not supplied or cannot be matched to known values, data interpretation derives their content from the decimal coordinates through a lookup service.
Terms: dwc:countryCode, dwc:country, dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Country invalid (geospatial) example
The country or countryCode given cannot be matched to the vocabulary for country names.
Terms: dwc:country
Continent invalid (geospatial) example
The continent given cannot be matched to the vocabulary for continent names
Terms: dwc:continent
Coordinate rounded (geospatial) example
In the data interpretation the original coordinates are rounded to 6 decimals (~1m precision).
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Coordinate reprojected (geospatial) example
The original coordinates were successfully reprojected from a different geodetic datum to WGS84.
Terms: dwc:geodeticDatum
Coordinate reprojection suspicious (geospatial) example
Indicates successful coordinate reprojection according to provided datum, but which results in a datum shift larger than 0.1 decimal degrees.
Terms: dwc:geodeticDatum, dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Coordinate reprojection failed (geospatial) example
The given decimal latitude and longitude could not be reprojected to WGS84 based on the provided datum.
Terms: dwc:geodeticDatum, dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude
Coordinate uncertainty meters invalid (geospatial) example
The value given for Coordinate uncertainty in meters, indicating the radius of uncertainty around the given decimal coordinates, is not a valid number, or lies outside a plausible range.
Terms: dwc:coordinateUncertaintyInMeters
Coordinate precision invalid (geospatial) example
Indicates an invalid or very unlikely coordinates precision. The value is not a decimal number as expected, or it has an unusually low or high for a margin of uncertainty.
Terms: dwc:coordinatePrecision
Presumed negated longitude (geospatial) example
The supplied longitude value places the coordinates outside of the indicated country. Negating the longitude value would result in a country match.
Terms: dwc:decimalLongitude
Presumed negated latitude (geospatial) example
The supplied latitude value places the coordinates outside of the indicated country. Negating the latitude value would result in a country match.
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude
Presumed swapped coordinate (geospatial) example
Coordinates seem to be swapped when testing against the interpreted country.
Terms: dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimalLongitude, dwc:country
Depth min max swapped (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum depth appear to the swapped.
Terms: dwc:minimumDepthInMeters, dwc:maximumDepthInMeters
Depth non numeric (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum depth are non-numeric values and cannot be interpreted.
Terms: dwc:minimumDepthInMeters, dwc:maximumDepthInMeters
Depth unlikely (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum depth are negative or higher than 11000 (Mariana Trench depth in meters).
Terms: dwc:minimumDepthInMeters, dwc:maximumDepthInMeters
Depth not metric (geospatial) example
Set if supplied depth is not given in the metric system, for example using feet instead of meters.
Terms: dwc:minimumDepthInMeters, dwc:maximumDepthInMeters
Elevation non numeric (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum elevation are non-numeric values and cannot be interpreted.
Terms: dwc:minimumElevationInMeters, dwc:maximumElevationMeters
Elevation min max swapped (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum elevation appear to the swapped.
Terms: dwc:minimumElevationInMeters, dwc:maximumElevationInMeters
Elevation not metric (geospatial) example
Set if supplied elevation is not given in the metric system, for example using feet instead of meters.
Terms: dwc:minimumElevationInMeters, dwc:maximumElevationInMeters
Zero occurrence records are flagged with the following geospatial issues on GBIF as of the writing of this post.
Elevation unlikely (geospatial) example
The values for minimum and maximum elevation are above the troposphere (17000 m) or below Mariana Trench (11000 m).
Terms: dwc:minimumElevationInMeters, dwc:maximumElevationInMeters
Continent country mismatch (geospatial) example
The interpreted continent and country do not match up.
Terms: dwc:continent, dwc:countryCode, dwc:country
Continent derived from coordinates (geospatial) example
If no value is supplied for the continent or if the values cannot be matched against a known vocabulary, data interpretation derives the continent from the decimal coordinates.
Terms: dwc:continent, dwc:decimalLatitude, dwc:decimal Longitude
**Taxonomic Issues**
Taxon match higherrank (taxonomic) example
The record can be matched to the GBIF taxonomic backbone at a higher rank, but not with the scientific name given.
Terms: dwc:scientificName,dwc:kingdom,dwc:phylum, dwc:class, dwc:order, dwc:family, dwc:genus, dwc:subgenus, dwc:specificEpithet, dwc:infraspecificEpithet, dwc:taxonRank
Reasons include:
- The name is new, and not available in the taxonomic datasets yet
- The name is missing in the backbone’s taxonomic sources for others reasons
- Formatting or spelling of the scientific name caused interpretation errors
Taxon match none (taxonomic) example
Matching to the taxonomic backbone cannot be done cause there was no match at all or several matches with too little information to keep them apart (homonyms).
Terms: dwc:scientificName,dwc:kingdom,dwc:phylum, dwc:class, dwc:order, dwc:family, dwc:genus, dwc:subgenus, dwc:specificEpithet, dwc:infraspecificEpithet, dwc:taxonRank
Taxon match fuzzy (taxonomic) example
Matching to the taxonomic backbone can only be done using a fuzzy, non exact match.
Terms: dwc:scientificName,dwc:kingdom,dwc:phylum, dwc:class, dwc:order, dwc:family, dwc:genus, dwc:subgenus, dwc:specificEpithet, dwc:infraspecificEpithet, dwc:taxonRank
[Edit 2023-09-21 New flags added]
Scientific name and ID inconsistent (taxonomic) example
The scientificName provided in the occurrence record does not precisely match the name in the registered checklist when using the scientificNameID, taxonID or taxonConceptID to look it up. Publishers are advised to check the IDs are correct, or update the formatting of the names on their records.
Terms: dwc:scientificName,dwc:scientificNameID,dwc:taxonID,dwc:taxonConceptID
Taxon match name and ID ambiguous (taxonomic) example
The GBIF Backbone concept was found using the scientificNameID, taxonID or taxonConceptID, but it differs from what would have been found if the classification names on the record were used. This may indicate a gap in the GBIF backbone, a poor mapping between the checklist and the backbone, or a mismatch between the classification names and the declared IDs (scientificNameID or taxonConceptID) on the occurrence record itself.
Terms: dwc:scientificName,dwc:scientificNameID,dwc:taxonID,dwc:taxonConceptID
Scientific name ID not found (taxonomic) example
The scientificNameID matched a known pattern, but it was not found in the associated checklist. The backbone lookup was performed using either the names or a different ID field from the record. This may indicate a poorly formatted identifier or may be caused by a newly created ID that isn’t yet known in the version of the published checklist.
Terms: dwc:scientificNameID
Taxon concept ID not found (taxonomic) example
The taxonConceptID matched a known pattern, but it was not found in the associated checklist. The backbone lookup was performed using either the names or a different ID field from the record. This may indicate a poorly formatted identifier or may be caused by a newly created ID that isn’t yet known in the version of the published checklist.
Terms: dwc:taxonConceptID
Taxon ID not found (taxonomic) example
The taxonID found matched a known pattern, but it was not found in the associated checklist. The backbone lookup was performed using either the names or a different ID field from the record. This may indicate a poorly formatted identifier or may be caused by a newly created ID that isn’t yet known in the version of the published checklist.
Terms: dwc:taxonID
Taxon match scientific name ID ignored (taxonomic) example
The scientificNameID was not used when mapping the record to the GBIF backbone. This may indicate one of: (1) The ID uses a pattern not configured for use by GBIF (2) The ID did not uniquely identify a concept in the checklist (3) The ID found a concept in the checklist that did not map to the backbone (4) A different ID was used, or the record names were used, as no ID lookup successfully linked to the backbone
Terms: dwc:scientificNameID
Taxon match taxon concept ID ignored (taxonomic) example
The taxonConceptID was not used when mapping the record to the GBIF backbone. This may indicate one of: (1) The ID uses a pattern not configured for use by GBIF (2) The ID did not uniquely identify a concept in the checklist (3) The ID found a concept in the checklist that did not map to the backbone (4) A different ID was used, or the record names were used, as no ID lookup successfully linked to the backbone
Terms: dwc:taxonConceptID
Taxon match taxon ID ignored (taxonomic) example
The taxonID was not used when mapping the record to the GBIF backbone. This may indicate one of: (1) The ID uses a pattern not configured for use by GBIF (2) The ID did not uniquely identify a concept in the checklist (3) The ID found a concept in the checklist that did not map to the backbone (4) A different ID was used, or the record names were used, as no ID lookup successfully linked to the backbone
Terms: dwc:taxonID
**Date Issues**
Recorded date invalid (date) example
The recording date given cannot be intrepreted because is invalid.
Terms: dwc:eventDate, dwc:year, dwc:month, dwc:day
Reasons include:
- A non-existing date (e.g “1995-04-34”)
- Missing date parts (e.g. Event date without year).
- The date format does not follow the ISO 8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD)
Recorded date mismatch (date) example
The recording date specified as the eventDate string and the individual year, month, day are contradicting.
Terms: dwc:eventDate, dwc:year, dwc:month, dwc:day
Identified date unlikely (date) example
The identification date is in the future or before Linnean times (1700).
Terms: dwc:dateIdentified
Recorded Date Unlikely (date) example
The recording date is highly unlikely, falling either into the future or representing a very old date before 1600 that predates modern taxonomy.
Terms: dwc:eventDate, dwc:year, dwc:month, dwc:day
Multimedia date invalid (date) example
The creation date given cannot be intrepreted because is invalid.
Terms: dc:created
Reasons include:
- A non-existing date (e.g “1995-04-34”)
- Missing date parts (e.g. Event date without year).
- The date format does not follow the ISO 8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD)
Identified date invalid (date) example
The identification date given cannot be intrepreted because is invalid.
Terms: dwc:dateIdentified
Reasons include:
- A non-existing date (e.g “1995-04-34”)
- Missing date parts (e.g. without year).
- The date format does not follow the ISO 8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD)
Modified date invalid (date) example
A (partial) invalid modified date is given.
Terms: dc:modified
Reasons include:
- A non-existing date (e.g “1995-04-34”)
- Missing date parts (e.g. without year).
- The date format does not follow the ISO 8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD)
Modified date unlikely (date) example
The modified date given is in the future or predates unix time (1970).
Terms: dc:modified
Georeferenced date invalid (date) example
The georeference date given cannot be intrepreted because it is invalid.
Terms: dwc:georeferencedDate
Reasons include:
- A non-existing date (e.g “1995-04-34”).
- Missing date parts (e.g. without year).
- The date format does not follow the ISO 8601 standard (YYYY-MM-DD)
Georeferenced date unlikely (date) example
The georeference date given is in the future or before Linnean times (1700).
Terms: dwc:georeferencedDate
**Vocabulary Issues**
Basis of record invalid (vocabulary) example
The given basis of record is impossible to interpret or very different from the recommended vocabulary: http://rs.gbif.org/vocabulary/dwc/basis_of_record.xml
Terms: dwc:basisOfRecord
Type status invalid (vocabulary) example
The given type status is impossible to interpret or very different from the recommended vocabulary: https://rs.gbif.org/vocabulary/gbif/type_status.xml
Terms: dwc:typeStatus
Occurrence status unparsable (vocabulary) example
The given occurenceStatus value cannot be interpreted; it does not match any of the known (vocabulary) values that indicate the presence or absence of a species at collection or observation event.
Terms: dwc:occurrenceStatus
**GRSciColl-related Issues**
Ambiguous institution (GRSciColl) example
Multiple institutions were found in GRSciColl with the same level of confidence and it can’t be determined which one should be accepted. For example, there are several institutions with the same code and country. See this FAQ on how to avoid ambiguous matches.
Terms: dwc:institutionCode, dwc:institutionID
Ambiguous collection (GRSciColl) example
Multiple collections were found in GRSciColl with the same level of confidence and it can’t be determined which one should be accepted. For example, there are several collections belonging to the same institution with the same code. See this FAQ on how to avoid ambiguous matches.
Terms: dwc:collectionCode, dwc:collectionID
Institution match none (GRSciColl) example
No macth was found in GRSciColl. Either the entry doesn’t exists in GRSciColl or it has a different code. Check GRSciColl and request update if needed.
Terms: dwc:institutionCode, dwc:institutionID
Collection match none (GRSciColl) example
No macth was found in GRSciColl. Either the entry doesn’t exists in GRSciColl or it has a different code. Check GRSciColl and request update if needed.
Terms: dwc:collectionCode, dwc:collectionID
Institution match fuzzy (GRSciColl) example
A match was found in GRSciColl but it was matched fuzzily. To know more about why this has happened you can use the lookup API to see see the “reasons” returned in the response. A common case is when the name is used instead of the code or the identifier. To avoid fuzzy matches, publishers should use identifiers in additon to codes. More details available in this FAQ.
Terms: dwc:institutionCode, dwc:institutionID
Collection match fuzzy (GRSciColl) example
A match was found in GRSciColl but it was matched fuzzily. To know more about why this has happened you can use the lookup API to see see the “reasons” returned in the response. A common case is when the name is used instead of the code or the identifier. To avoid fuzzy matches, publishers should use identifiers in additon to codes. More details available in this FAQ.
Terms: dwc:collectionCode, dwc:collectionID
Institution collection mismatch (GRSciColl) example
At least one possible collection match was found in GRSciColl but none of them belong to the institution matched.
Terms: dwc:collectionCode, dwc:collectionID, dwc:institutionCode, dwc:institutionID
Different owner institution (GRSciColl) example
The institution doesn’t match the owner institution.
Terms: dwc:ownerInstitutionCode, dwc:institutionCode, dwc:institutionID
**Other Issues**
Individual count invalid (individual count) example
Individual count value not parsable into a positive integer.
Terms: dwc:individualCount
Individual count conflicts with occurrence status (individual count) example
The values given for the individual count and for the status of the occurrence (present/absent) contradict each other (e.g. the count is 0 but the status says “present”).
Terms: dwc:individualCount, dwc:occurrenceStatus
Occurrence status inferred from individual count (occurrence status) example
The present/absent status of the occurrence was inferred from the individual count value because no status value was supplied explicitly. An individual count of 0 is interpreted as status=“absent”, a value > 0 as “present”
Terms: dwc:individualCount, dwc:occurrenceStatus
References URI invalid (uri) example
The references URL cannot be resolved, and may be malformed or contain invalid characters. If there is more than one URL, the values have to be separated by a pipe symbol “|”.
Terms: dc:references
Multimedia URI invalid (uri) example
The multimedia URL cannot be resolved, and may be malformed or contain invalid characters. If there is more than one URL, the values have to be separated by a pipe symbol “|”.
Terms: dwc:associatedMedia
Interpretation error (interpretation) example
An error occurred during interpretation, leaving the record interpretation incomplete.
Terms: GBIF interpretation
Occurrence status inferred from Basis Of Record (interpretation) example
The occurrence status of preserved specimens (museum specimens) is assumed to be “present” (not absent). With other records occurrence status is usually inferred from from dwc:individualCount.
Terms: GBIF interpretation, dwc:individualCount
Checklists issues and flags [Edit from 2023-01-19]
The GBIF system also flags taxon records coming from checklists. You can search and select checklist records by flags in our Species search interface:
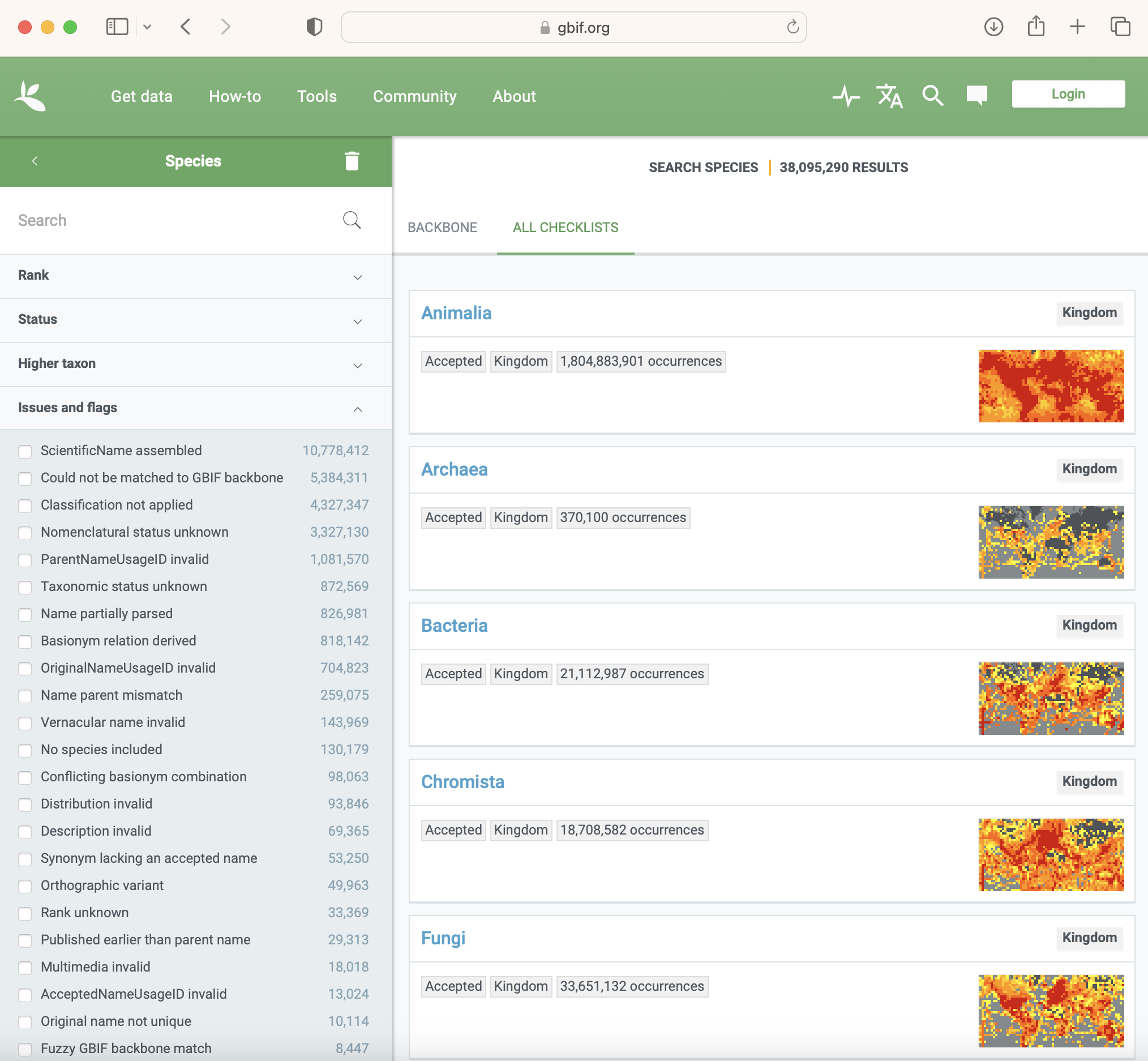
See the definitions below:
Name unparsable (checklist) example
The value in the field flagged couldn’t be parsed by the GBIF system. You can check if a scientific name can be parsed with our name parser tool: https://www.gbif.org/tools/name-parser
Terms: any name field
Name partially parsed (checklist) example
The value in the field flagged could only be partially parsed by the GBIF system. You can check if a scientific name can be parsed with our name parser tool: https://www.gbif.org/tools/name-parser
Terms: any name field
ParentNameUsageID invalid (checklist) example
The value for the ParentNameUsageID doesn’t correspond to a valid entry in the list. Check that the parentNameUsageID points to an existing taxon entry within the checklist (parentNameUsageID should contain the value of the taxonID of the parent taxon in the same checklist)
Terms: dwc:parentNameUsageID
AcceptedNameUsageID invalid (checklist) example
The value for the acceptedNameUsageID could not be resolved. Check that the acceptedNameUsageID points to an existing taxon entry within the checklist (for synonyms or misapplied named, acceptedNameUsageID should contain the value of the taxonID of the accepted/valid taxon name in the checklist)
Terms: dwc:acceptedNameUsageID
OriginalNameUsageID invalid (checklist) example
The value for originalNameUsageID could not be resolved. Check that the originalNameUsageID points to an existing taxon entry within the checklist (originalNameUsageID should contain the value of the taxonID of the scientificName in the checklist that represents the name originally established under the rules of the associated nomenclatural code, e.g. the basionym)
Terms: dwc:originalNameUsageID
Rank unknown (checklist) example
The value for taxonRank could not be interpreted. Check if you can map the value to one of the accepted taxon rank values
Terms: dwc:taxonRank
Nomenclatural status unknown (checklist) example
The value for nomenclaturalStatus could not be interpreted. Check if you can map the value to one of the accepted nomenclatural status values
Terms: dwc:nomenclaturalStatus
Taxonomic status unknown (checklist) example
The value for taxonomicStatus could not be interpreted. Check if you can map the value to one of the accepted taxonomic status values
Terms: dwc:TaxonomicStatus
ScientificName assembled (checklist) example
The scientific name was assembled from the individual name components (e.g. genus name, species epithet, authors), and not supplied as a whole. This is simply for information, publishers can ignore it.
Terms: dwc:scientificName
Chained synonym (checklist) example
The record is a synonym which has another synonym as it’s accepted name. The GBIF system resolves such chains and links every synonym to the final accepted name. Check that synonyms always point to accepted names.
Terms: dwc:acceptedNameUsageID
Basionym author mismatch (checklist) example
The authorship of the original name does not match the authorship in brackets of the taxon name. This flags the relationship between the two names as suspicious, based on the formal rules defined by nomenclatural codes.
Terms: dwc:scientificName, dwc:scientificNameAuthorship, dwc:originalNameUsage
Classification parent cycle (checklist) example
The child-parent relationships between taxon names result in a cycle that needs to be resolved/cut. The classification should be a tree.
Terms: dwc:parentNameUsageID
Classification not applied (checklist) example
The denormalized classification of the checklist, i.e. values for terms like dwc:family or dwc:phylum, could not be applied to the name safely. This usually happens if there is also a normalised parentNameUsageID-based classification given with unspecified ranks.
Terms: dwc:parentNameUsageID
Vernacular name invalid (checklist) example
At least one part of a vernacular name attached to this taxon name, linked from the Vernacular Names extension, could not be interpreted. This usually happens when the name was blank, but it is also flagged if other controlled values such as language, lifestage, plural or sex in a Vernacular Name record cannot be interpreted.
Terms: dwc:vernacularName and Vernacular Names extension http://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/vernacularname.xml
Description invalid (checklist) example
At least one description record for this taxon name, linked from the Taxon Description extension, could not be interpreted because the mandatory description was missing or the language field was invalid.
Terms: Taxon Description extension http://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/description.xml
Distribution invalid (checklist) example
At least one species distribution record for this taxon name, linked from the Species Distribution extension, could not be interpreted.
Terms: Species Distribution extension https://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/distribution.xml
Species profile invalid (checklist) example
At least one species profile record for this taxon name, linked from the Species Profile extension, could not be interpreted.
Terms: Species Profile extension https://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/speciesprofile_2019-01-29.xml
Multimedia invalid (checklist) example
At least one multimedia extension record attached to this taxon name could not be interpreted. This covers multimedia coming in through various extensions, including Audubon core, Simple images or multimedia or EOL media.
Terms: See https://data-blog.gbif.org/post/gbif-multimedia/
Bibliographic references invalid (checklist) example
At least one bibliographic reference for this taxon name, linked from the Literature References extension, could not be interpreted.
Terms: Literature References Extension https://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/references.xml
Alternative identifiers invalid (checklist) example
At least one alternative identifier for this taxon name, linked from the Alternative Identifiers extension, could not be interpreted.
Terms: Alternative Identifiers extension https://rs.gbif.org/extension/gbif/1.0/identifier.xml
Could not be matched to GBIF backbone (checklist) example
The interpretation of the taxonomic name could not find an existing equivalent, or near-enough match, in the GBIF taxonomic backbone. If the taxon name is newly described or a recent recombination, this is expected, until the new name can be integrated into the backbone taxonomy. You can check how a scientific name is matched against the backbone taxonomy using our species name matching tool: https://www.gbif.org/tools/species-lookup
Terms: dwc:scientificName
Fuzzy GBIF backbone match (checklist) example
Name match to the GBIF backbone taxonomy could only be done using a fuzzy, non exact match.
Terms: dwc:scientificName
Synonym lacking an accepted name (checklist) example
The taxon name is explicitly marked as a synonym, but lacking a reference to the corresponding accepted name. If the accepted name is contained in the same data source, consider adding a reference to it.
Terms: dwc:TaxonomicStatus, dwc:acceptedNameUsageID
Accepted name not unique (checklist) example
The synonym record provides the accepted name as verbatim text, rather than as a cross-reference. The verbatim name is ambiguous and could refer to several different records in GBIF’s backbone taxonomy.
Terms: dwc:acceptedNameUsage
Parent name not unique (checklist) example
The record provides the name of the taxonomic parent as verbatim text, rather than as a cross-reference. The verbatim name is ambiguous and could refer to several different records in GBIF’s backbone taxonomy.
Terms: dwc:parentNameUsage
Original name not unique (checklist) example
The record provides the original name of the taxon (e.g. basionym) as verbatim text, rather than as a cross-reference. The verbatim name is ambiguous and could refer to several different records in GBIF’s backbone taxonomy.
Terms: dwc:originalNameUsage
Relationship missing (checklist) example
There were problems representing all name relationships, i.e. the link to the parent, accepted and/or original name. The interpreted record in GBIF is lacking some of the original source relation.
Terms: dwc:originalNameUsage, dwc:parentNameUsage, dwc:acceptedNameUsage, dwc:acceptedNameUsageID, dwc:TaxonomicStatus, dwc:parentNameUsageID
Basionym relation derived (GBIF backbone) example
The record in GBIF has a relationship to an original name (basionym) that was derived from name & authorship comparison, but did not exist explicitly in the source data. This will only be flagged in programmatically generated GBIF backbone records of name usages. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Conflicting basionym combination (GBIF backbone) example
There have been more than one accepted name in a homotypical basionym group of names. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Terms: dwc:scientificName
No species included (GBIF backbone) example
The group (currently only genera are tested) is lacking any accepted species. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Name parent mismatch (GBIF backbone) example
The (accepted) bi/trinomial name does not match the parent name and should be recombined into the parent genus/species. For example the species Picea alba with a parent genus Abies is a mismatch, and should be replaced by Abies alba. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Orthographic variant (GBIF backbone) example
An entry in the backbone is suspected to be only a spelling variation of an otherwise existing name. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Homonym (GBIF backbone) example
A not synonymized homonym exists for this name in some other backbone source which have been ignored at build time. GBIF backbone specific issue.
Published earlier than parent name (GBIF backbone) example
A bi/trinomial name was seemingly published earlier than the parent genus/species. This might indicate a homonym issue, or that the name should rather be a recombination. GBIF backbone specific issue.
